Storey's 'Must-Have Features' for a Chicken Shelter
 Monday, February 10, 2020 at 1:43PM
Monday, February 10, 2020 at 1:43PM
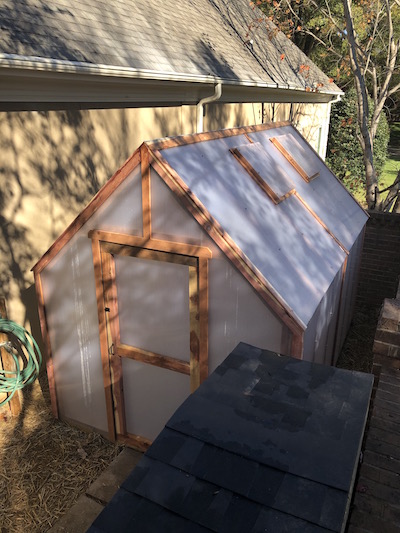
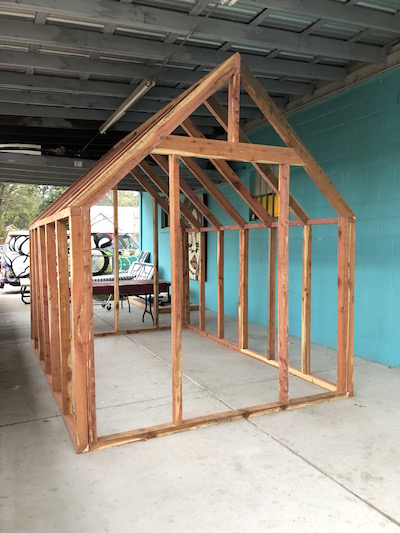
“Storey’s Guide to Raising Chickens” has long been the undisputed authority on the subject, and every backyard flock owner should own a copy. This indispensable resource has the correct answers for everything from breed selection to bedding. Chapter three covers shelter in detail, and it gives the determined and patient reader enough useful material to move forward with confidence. And for the busy would-be chicken owners out there - rapidly skimming the pages for a quick grasp what’s involved with a backyard chicken coop - the book has generously provided this simple checklist. But whether you’re raising dozens and dozens of chickens out in the country, or three hens in your suburban backyard, you’ll be wise to check off each one of these ‘Must-Have Features’ from the chapter on chicken shelter.
-Provides enough space for the number of birds. Overcrowding causes all sorts of problems in a chicken coop, from foul odor and disease to bullying and cannibalism.
-Good Ventilation. This introduces oxygen-rich fresh air, and helps remove moist, stale air from inside the coop, which often contain unhealthy levels of carbon dioxide and ammonia. Consider a coop design with good airflow that allows dust particles and airborne, disease-causing organisms to dissipate.
-draft free. Blocking cold drafts on the north side of the coop makes a huge difference in keeping your hens comfortable during the winter months.
-maintains a comfortable temperature. An ideal site for your chicken coop would be shaded during the hottest part of the day during summer, and allow maximum sunlight to reach the flock during winter. Choose a coop design that has both excellent ventilation and protection from cold wind gusts.
-protects the chickens from wind and sun. Build your chicken shelter where it will be shaded during the hottest part of the day, and consider planting shrubs as a windbreak to help mitigate exposure to prevailing winds.
-keeps out rodents, wild birds, and predatory animals. A chicken coop should have a sturdy frame capable of easily thwarting large predators like dogs and coyotes, and galvanized steel mesh covering every possible point of entry to keep out smaller bandits like wild birds, snakes and rodents. The hardware cloth should be buried about 12” deep around the entire perimeter of the coop to keep out nocturnal digging predators like raccoons.
-offers plenty of sunlight during the day. Consider a design like the Garden Coop, that has tinted clear polycarbonate roof panels that allow lots of sunlight inside the coop during the cold months when the hens need it most, and still help block the intensity of bright summer days.
-has adequate roosting space. Give your hens a couple of roost branches placed at different heights so that the peck order can be easily maintained inside your coop. Live branches about 4” in diameter allow your birds to roost more comfortably than smaller diameter dowel rods or a milled pieces of lumber.
-includes clean nests for the hens to lay eggs. Nothing spoils the fun of harvesting your backyard eggs like finding them covered in poop. If possible, try to have at least one nesting box for every three or four hens.
-has sanitary feed and water stations. Make sure your feeder and waterer are the right size for your flock, and hang them so they’re accessible for every bird, but still far enough from the ground so they aren’t constantly soiled with scratched bedding.
-is situated where drainage is good. Note where stormwater flows when it rains, and either site your chicken coop to avoid the runoff altogether, or if this isn’t possible, dig a swale or ditch to channel stormwater away from the coop.